Result
- ✨ Individual Rank: 32nd / 250 participants
- 🥉 Team Rank: 11th / 38 teams
Task Description
Competition participants should identify 18 classes correctly and competition grading criteria is based on F1 Score.
Goal is to classify Age Range, Biological Sex, Face Mask
- There are 3 classes for the Age Range: Lower than 30, Between 30 and 59, Above 60.
- Biological Sex class is consisted of 2 classes which are Male and Female.
- Thera are 3 classes for Face Mask which are: Wear, Incorrectly Wear, Not wear.
Development Environment Settings
-
Had consistent CUDA error on Upstage server which remained unsolved until the end.
- This was CNN Model that works on CPU Device on provided Upstage server.
- But 4 types of error arose when the same model & code was run on GPU Device. Sometimes the error occurred on fully connected layer(fc1), but other times the error occurred on convolutional layer(conv2).
- 🔗 CUDA error: an illegal instruction
- 🔗 CUBLASSTATUSALLOC_FAILED
- 🔗 CUDNNSTATUSMAPPING_ERROR
- 🔗 CUBLASSTATUSEXECUTION_FAILED
- After debugging for two days, I decided to proceed the competition on Colab Pro + account.
Choosing and Comparing Model
- I focused on my role to provide backbone code that could be experimented by other teammates.
- Thus minimum amount of albumentation/transformation was applied, whereas different types of models were alternated one by one.
- From torchvision library and timm library, model performance SOTA models were compared for the competition's dataset.
- It is proved that tfefficientnetb4 from the timm library was the most adaquate model for the competition.
- For the comparison purpose, the hyperparameters, optimizers, train vs valid split ratio were not differentiated according to the models.
- The table was provided in form of Google Spreadsheet to my teammates so that they can compare models according to Eval F1 score or Validation F1 score.
- Furthermore it showed that setting more than 10 epochs did improve train accuracy and validation accuracy, but didn't improve the model's performance in terms of Eval F1 score.
| Eval F1 | Valid F1 | Pretrained Model | Train Albumentation | Valid Albumentation | Test Albumentation | Class Division | Train: Valid Split Ratio | Train Batch Size | Epoch | Learning Rate | Weight Decay | Criterion (Loss) | Optimizer | Scheduler | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7111 | 0.9279 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(height = 260, width = 200, p=1.0), HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(height = 260, width = 200, p=1.0), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize((260,200), Image.BILINEAR), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.53087462, 0.45734182, 0.42477556), std=(0.23390616, 0.2311533, 0.23603857)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 32 | 9 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/31 |
| 0.6975 | 0.8737 | tfefficientnetb3 | Resize(height = 260, width = 200, p=1.0), HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(height = 260, width = 200, p=1.0), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize((260,200), Image.BILINEAR), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.53087462, 0.45734182, 0.42477556), std=(0.23390616, 0.2311533, 0.23603857)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 32 | 9 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/31 |
| 0.7119 | 0.9162 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(height = 350, width = 350, p=1.0), HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(height = 350, width = 350, p=1.0), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize((350,350), Image.BILINEAR), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.51573701, 0.46091698, 0.43106825), std=(0.23412625, 0.23709222, 0.24571251)) | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 8 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/30 |
| 0.6028 | 0.8756 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 10 | 1e-1 | 1e-5 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | SGDP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/29 |
| 0.7197 | 0.8949 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 4 | 1e-1 | 1e-5 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | SGDP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/29 |
| 0.7260 | 0.8903 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 10 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/27 |
| 0.7259 | 0.903 | tfefficientnetb4 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 17 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/28 |
| 0.7170 | 0.886 | resnext50_32x4d | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 32 | 10 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/26 |
| 0.6870 | 0.8922 | vitbasepatch16_384 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 384, width = 384), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 384, width = 384), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | transforms.Compose([ Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop((384,384)), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), ]) | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 10 | 1e-4 | 1e-6 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/26 |
| 0.6820 | 0.896 | vitlargepatch32224in21k | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height =224, width = 224), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height =224, width = 224), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | transforms.Compose([ Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop((224,224)), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), ]) | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 3 | 1e-4 | 1e-6 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/27 |
| 0.6730 | 0.856 | resnet50 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0) | Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 32 | 10 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/26 |
| 0.4423 | 0.8583 | vitbasepatch16_384 | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1], p=1.0), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), Resize(384, 384, p=1.0), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | Resize(imgsize[0], imgsize[1]), CenterCrop(height = 350, width = 350), # add centercrop Resize(384, 384, p=1.0), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std, maxpixelvalue=255.0, p=1.0), ToTensorV2(p=1.0), | transforms.Compose([ Resize((512, 384), Image.BILINEAR), transforms.CenterCrop((350,350)), Resize((384, 384), Image.BILINEAR), ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)), ]) | 18 | 0.9 : 0.1 | 16 | 10 | 3e-4 | 1e-2 | FocalLoss(gamma = 5) | AdamP | MultiStepLR | 2021/08/27 |
| 0.0550 | 0.99 0.92 0.95 | resnet50 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) | transforms.Resize(256), transforms.CenterCrop(224), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) | 3 x 3 x 2 | 0.6 : 0.2 : 0.2 | 256 | 10 | 1e-4 | - | CrossEntropyLoss | Adam | StepLR | 2021/08/25 |
How to resolve the Class Imbalance of train dataset
- Females outnumbered males (1700 females vs 1000 males)
- There were 200 individuals that were Age of 60 out of total 2700 individuals. They were the only individuals that consisted of the Class 60 and Above.
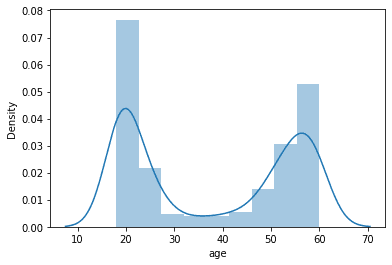
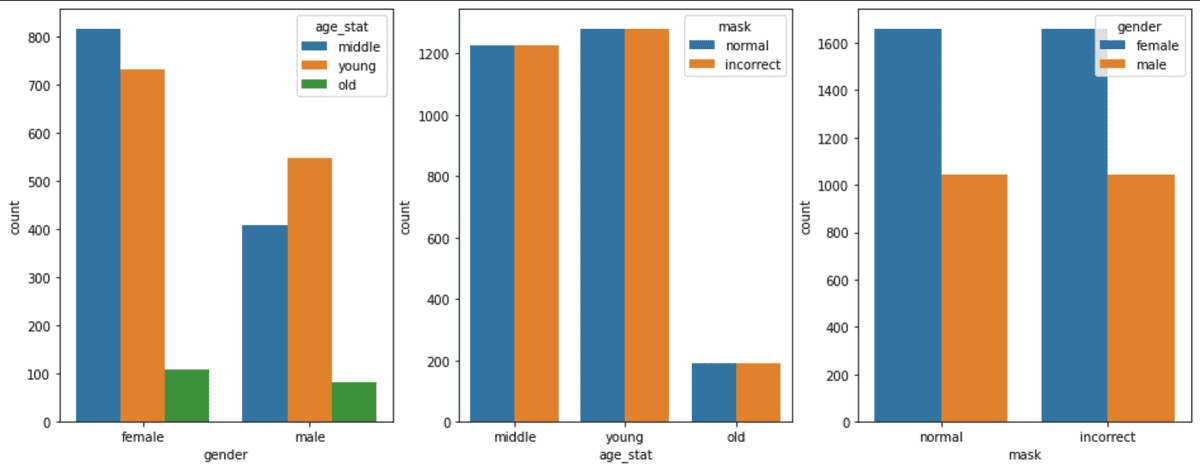
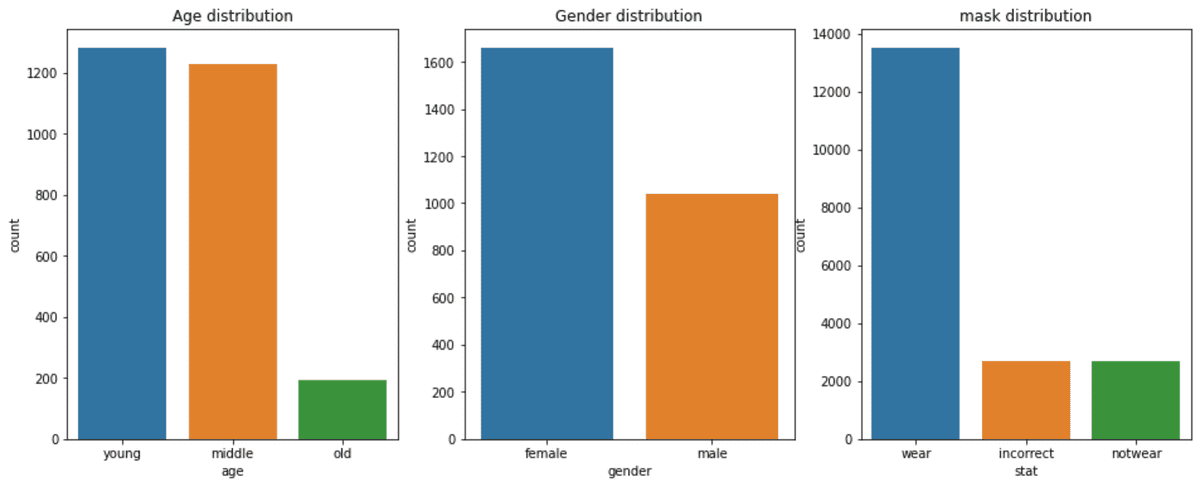
- Class of 60 and Above are consisted of only 17% of the total dataset.
- Mask Class is distributed as Wear 7 : Incorrect 1 : Not Wear 1
- RGB Mean was [0.56019358 0.52410121 0.501457]
- RGB Standard Deviation was [0.23318603 0.24300033 0.24567522]
- Out of 18 classes, there were two classes that consisted of only 0.44%(83 pics). There were also two classes that consisted of 20%(2000 pics).
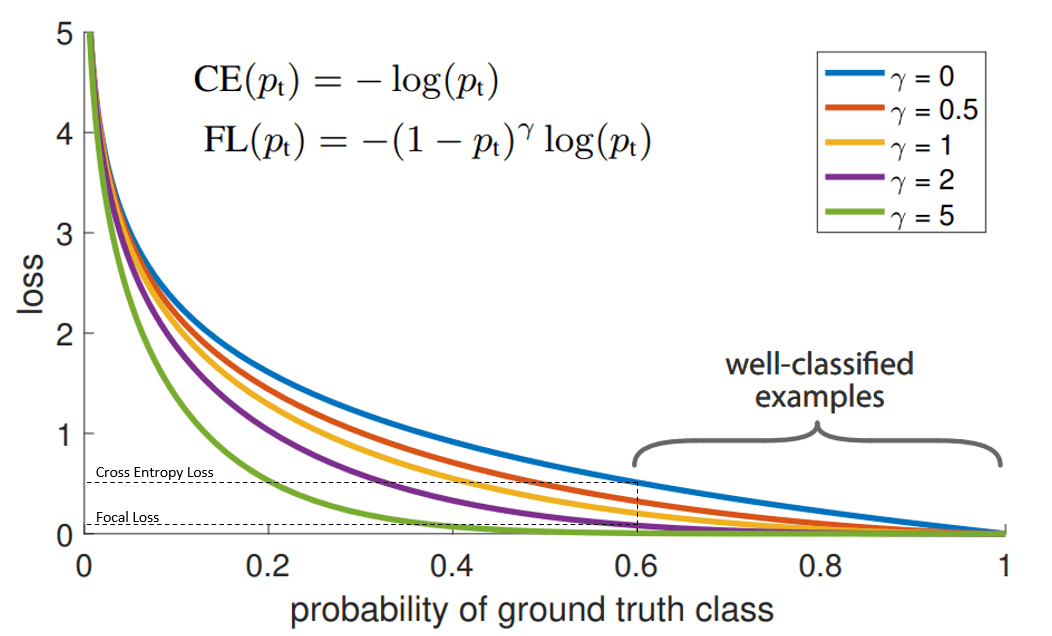
Choosing Loss for the Class Imbalance
I decided to use FocalLoss in order to resolve such class imbalance. Compared to cross entropy loss, Focal Loss was purported to reduce the proportion of background on the training image which definitely outnumbered the size of the objects in the dataset. Focal Loss with gamma value of 5 outperformed Cross Entropy Loss.
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight=None, gamma=2., reduction='mean'):
nn.Module.__init__(self)
self.weight = weight
self.gamma = gamma
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, input_tensor, target_tensor):
log_prob = F.log_softmax(input_tensor, dim=-1)
prob = torch.exp(log_prob)
return F.nll_loss(
((1 - prob) ** self.gamma) * log_prob,
target_tensor,
weight=self.weight,
reduction=self.reduction
)Adding Dataset to resolve class imbalance
- Also, in order to resolve the class imbalance I decided to add external dataset for the Age of 60 from All-Age-Faces-Dataset.
- Using the MaskTheFace opensource project, User can arbitrarily choose the color, color weight, patterns and the types of mask.
- From two open-source projects, I constructed external dataset like the following:
| normal | mask1 | mask2 | mask3 | mask4 | mask5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|
- By adding 646 males and 620 females who were age 60 and above, I thought this would have helped the model's performance on age classification.
- The format of the added image folder, the format of the added image information on
train.csvadhered to according to the competition's provided format. - For example, previous train dataset started with id number of
0xxxxxIndividual ids. Additional external train dataset were concat where male id starts with1xxxxxand female ids starts with2xxxxx, in order to separate itself from the original dataset. - The following is the code for randomizing mask pattern and color weight for individuals. The project did provide batch processing, but it did not provide function for randomizing both pattern and color.
- Unfortunately the following code didn't help the model performance to improve. It was both experimented by me and my teammates, but the f1_score oscilated in between the significance probability level 0.05.
import os
import random
import glob
import itertools
from IPython.display import clear_output
BASE_COMMAND = "python mask_the_face.py"
PATTERN_PATH = "/Users/noopy/Documents/dataset-kitchen/_clones/MaskTheFace/masks/textures"
OLD_MALE_PATH = "/Users/noopy/Documents/dataset-kitchen/_clones/_DATASET/Old-Male/AGEFACE"
OLD_FEMALE_PATH = "/Users/noopy/Documents/dataset-kitchen/_clones/_DATASET/Old-Female/AGEFACE"
mask_types = ["surgical_green", "surgical_blue", "N95", "KN95", "cloth"]
# find all items in the folder
images_paths = glob.glob(os.path.join(OLD_MALE_PATH, "*"))
print(len(images_paths))
# repeat the list images_path by 5 times
images_paths = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(itertools.repeat(x, 5) for x in images_paths))
print(len(images_paths))
# get random hex values color
def get_random_color():
return '#%02x%02x%02x' % (random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255))
mask_types = ["surgical_green", "surgical_blue", "N95", "KN95", "cloth"]
# get folders in side of pattern_path
folders = [os.path.join(PATTERN_PATH, folder) for folder in os.listdir(PATTERN_PATH)]
patterns = []
for folder in folders:
# collect all jpg and png items inside of the folder
patterns += glob.glob(os.path.join(folder, "*.jpg"))
patterns += glob.glob(os.path.join(folder, "*.png"))
for path in images_paths:
print(path)
# chose random item from the list
mask_type = mask_types[random.randint(0, len(mask_types) - 1)]
# range color weight between 0.2 to 0.7
color_weight = random.uniform(0.2, 0.7)
# define random hex color
color_hex = get_random_color()
# get random path out of patterns
patterns_path = random.choice(patterns)
# get random pattern weight out of [0, 0.5, 1], choose more weight on 0
pattern_weight = random.choice([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0])
# generate the command
command = f"{BASE_COMMAND} \
--path '{path}' \
--mask_type random \
--pattern '{patterns_path}' \
--pattern_weight {pattern_weight} \
--color '{color_hex}' \
--color_weight {color_weight} \
--verbose"
# execute the command
os.system(command)
# clear the output
clear_output()Oversampling to Alleviate Class Imbalance.
- Since the class age 60 and above only included the age of 60, my teammates suggested to use age 58 & age 59 to relabeled as the class of age 60 and above.
- This oversampling attempt significantly improved the validation f1 score from 0.75 to 0.76.
Cropping face to reduce noise
🔗 LocatefaceboundingboxMTCNN_Retinaface.ipynb
- I thought it was important to reduce the background noise intervention for the train dataset. Therefore, it was essential to either Centercrop or extract the face data only from the image.
- I combined MTCNN that utilized GPU but with lower accuracy, Retinace that utilized CPU only but with higher accuracy.
- I shared the code with other Naver BoostCamp participants and it seems like many groups have implemented it.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
from facenet_pytorch import MTCNN
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from retinaface import RetinaFace
import glob
# make empty dataframe
df_image = pd.DataFrame({})
cnt = 0 # intialize iteration count
# padding value before cropping
X_PADDING = 20
Y_PADDING = 30 # gave more padding in order to include mask on the chin & hair style
# iterrate rows for the given training dataset
for index, row in tqdm(df_label.iterrows()):
# get default values
train_image_paths = []
id = row["id"]
gender = row["gender"]
race = row["race"]
age = row["age"]
profile = row["path"]
profile_path = os.path.join(TRAIN_IMGS_DATASET_PATH, profile)
# print(profile_path)
# get list of images from the given profile path
jpg_file_list = glob.glob(f"{profile_path}/*.jpg")
jpeg_file_list = glob.glob(f"{profile_path}/*.jpeg")
png_file_list = glob.glob(f"{profile_path}/*.png")
list_images = jpg_file_list + jpeg_file_list + png_file_list
# print(list_images)
for image_file_path in list_images:
cnt += 1
# read image and extract information using mtcnn
img = cv2.imread(image_file_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
boxes, probs, landmarks = mtcnn.detect(img, landmarks=True)
# default detection with mtcnn
if probs[0]:
# print("solved with mtcnn")
# save face bounding box information
xmin = int(boxes[0, 0]) - X_PADDING
ymin = int(boxes[0, 1]) - Y_PADDING
xmax = int(boxes[0, 2]) + X_PADDING
ymax = int(boxes[0, 3]) + Y_PADDING
# save landmark information
left_eye = landmarks[0, 0]
right_eye = landmarks[0, 1]
mouth_left = landmarks[0, 2]
mouth_right = landmarks[0, 3]
nose = landmarks[0, 4]
# if mtcnn fails, use retinaface
else:
result_detected = RetinaFace.detect_faces(image_file_path)
# print(result_detected)
# try retinaface to resolve,:
if type(result_detected) == dict:
print("resolving with retinaface: ", image_file_path)
# save face bounding box information
xmin = int(result_detected["face_1"]["facial_area"][0]) - X_PADDING
ymin = int(result_detected["face_1"]["facial_area"][1]) - Y_PADDING
xmax = int(result_detected["face_1"]["facial_area"][2]) + X_PADDING
ymax = int(result_detected["face_1"]["facial_area"][3]) + Y_PADDING
# save landmark information
face_landmarks = result_detected["face_1"]["landmarks"]
left_eye = face_landmarks["left_eye"]
right_eye = face_landmarks["right_eye"]
mouth_left = face_landmarks["mouth_left"]
mouth_right = face_landmarks["mouth_right"]
nose = face_landmarks["nose"]
# if both of the detection fails, center crop
elif type(result_detected) == tuple:
print("this one is causing trouble: ", image_file_path)
# manually set coordinates
# xmin = 50
# ymin = 100
# xmax = 350
# ymax = 400
xmin = 80
ymin = 50
xmax = 80 + 220
ymax = 50 + 320
# leave landmark information empty
face_landmarks = left_eye = right_eye = np.nan
mouth_left = mouth_right = nose = np.nan
# add row to the df_images with the extracted information
df_image = df_image.append(
{
"id":id,
"gender":gender,
"race":race,
"age":age,
"path": profile,
"image_file_path": image_file_path,
"xmin": xmin,
"ymin": ymin,
"xmax": xmax,
"ymax": ymax,
"left_eye": left_eye,
"right_eye": right_eye,
"mouth_left": mouth_left,
"mouth_right": mouth_right,
"nose": nose
}, ignore_index=True)
# print data information every 100 iterations
if cnt % 100 == 0:
print(df_image.shape)
print(df_image.info())
print(df_image.tail())- Landmark information and face coordinates were integrated with
train.csvfile for later image cropping: it purported to be processed in cv2 or PIL. - It did improve ViT models' performance. However, it turned out that extracting facial characteristics didn't improve the Efficientnet model's performance. Result turned out that center cropping (horizontal = 400, width = 200) pixel were more effective for efficientnet models. Center cropping with longer height included essential characteristics to include neck wrinkles & facial wrinkles to discern age class.
-
Pictures were often exceptionally cropped in small size. This was because MTCNN of Pytorch FaceNet often detected patterns of the mask or patterns of the clothes as eyes/nose/lips. These anomalies were later filtered by cropped pictures' width and height.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # read train_images.csv which contains predefined facial coordinate information df_train = pd.read_csv('./train_images.csv') df_train.head() x_range = df_train_new["xmax"] - df_train_new["xmin"] y_range = df_train_new["ymax"] - df_train_new["ymin"] # plot distribution of x_range plt.hist(x_range, bins=100) # check distribution statistics of x_range x_range.describe() # set minimum for the width by mean - 1.96 sigma (approximately bottom 3%) x_restriction = int(x_range.mean() - 1.96 * x_range.std()) + 1 # plot distribution of y_range plt.hist(y_range, bins=100) # set minimum for the height by mean - 1.96 sigma (approximately bottom 3%) y_restriction = int(y_range.mean() - 1.96 * y_range.std()) + 1 # get undersized cropped images that are under miniumum width and minum height df_train_too_small = df_train_new[(df_train_new["xmax"] - df_train_new["xmin"] < x_border) & (df_train_new["ymax"] - df_train_new["ymin"] < y_border)] df_train_too_small.info() # set xmin = 80, ymin = 50, xmax = 80 + 220, ymax = 50 + 320 for df_train_new that matches df_train_too_small df_train_new.loc[df_train_new["image_file_path"].isin(df_train_too_small["image_file_path"]), "xmin"] = 80.0 df_train_new.loc[df_train_new["image_file_path"].isin(df_train_too_small["image_file_path"]), "ymin"] = 50.0 df_train_new.loc[df_train_new["image_file_path"].isin(df_train_too_small["image_file_path"]), "xmax"] = 80.0 + 220.0 df_train_new.loc[df_train_new["image_file_path"].isin(df_train_too_small["image_file_path"]), "ymax"] = 50.0 + 320.0 # save fixed information df_train_new.to_csv('./train_images.csv', index=False) - Same process of detecting & cropping facial information was applied on the evaluation image dataset.
Other teammate's ideas & contributions
1. Applying Stratified K-fold
One thing to note is that stratified K-fold should have stopped more or less at 2nd or 3rd fold. After then, the model has already seen both the train and test set, therefore the further training should be halted.
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold , StratifiedKFold
for epoch in range(10):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
epoch_val_loss = 0
epoch_val_acc = 0
epoch_class_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_class_val_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_mask_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_mask_val_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_gender_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_gender_val_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_age_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
epoch_age_val_acc = [[] for i in range(18)]
stratified_kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
k_idx = 1
for train_index, validate_index in stratified_kfold.split(np.zeros(len(train_ages)), train_ages):
print(f'## Stratified_K-Fold :: {k_idx}')
k_idx += 1
train_dataset = torch.utils.data.dataset.Subset(dataset, train_index)
valid_dataset = torch.utils.data.dataset.Subset(dataset, validate_index)
valid_dataset = copy.deepcopy(valid_dataset)
valid_dataset.dataset.transform = transform_val
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=32,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0,
drop_last=True
)
val_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset,
batch_size = 32,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0
)
for i, data in tqdm(enumerate(train_loader), desc=f"epoch-{epoch}", total=len(train_loader)):
inputs, (labels, masks, genders, ages) = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs_mask, outputs_gender, outputs_age = model(inputs)
outputs_label = func_labels(outputs_mask, outputs_gender, outputs_age, device)
loss_masks = criterion(outputs_mask, masks)
loss_genders = criterion(outputs_gender, genders)
loss_ages = criterion(outputs_age, ages)
loss = loss_masks + loss_genders + loss_ages
epoch_loss += loss
acc = func_acc(outputs_label, labels)
epoch_acc += acc
epoch_class_acc = func_class_acc(outputs_label, labels, epoch_class_acc)
epoch_mask_acc = func_class_acc_mask(outputs_mask, masks, epoch_mask_acc)
epoch_gender_acc = func_class_acc_gender(outputs_gender, genders, epoch_gender_acc)
epoch_age_acc = func_class_acc_age(outputs_age, ages, epoch_age_acc)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, data in enumerate(val_loader):
val_inputs, (val_labels, val_masks, val_genders, val_ages) = data
val_outputs_mask, val_outputs_gender, val_outputs_age = model(val_inputs)
val_outputs_label = func_labels(val_outputs_mask, val_outputs_gender, val_outputs_age, device)
val_loss_mask = criterion(val_outputs_mask, val_masks)
val_loss_gender = criterion(val_outputs_gender, val_genders)
val_loss_age = criterion(val_outputs_age, val_ages)
val_loss = val_loss_mask + val_loss_gender + val_loss_age
epoch_val_loss += val_loss
val_acc = func_acc(val_outputs_label, val_labels)
epoch_val_acc += val_acc
epoch_class_val_acc = func_class_acc(val_outputs_label, val_labels, epoch_class_val_acc)
epoch_mask_val_acc = func_class_acc_mask(val_outputs_mask, val_masks, epoch_mask_val_acc)
epoch_gender_val_acc = func_class_acc_gender(val_outputs_gender, val_genders, epoch_gender_val_acc)
epoch_age_val_acc = func_class_acc_age(val_outputs_age, val_ages, epoch_age_val_acc)2. Applying Out-of-fold Ensemble
I believed that ensemble won't improve the model's performance, but it did! Teammates has tried both the hard voting ensemble(counting discrete integer of labels) and soft voting ensemble(summing predicted probabilities). We adapted soft voting as the favorable approach.
model_path = "/content/v4_stkfold5_epoch3_transformer_2th_000_loss_0.12.ckpt"
model1 = MyModel()
model1.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
model1.cuda()
model_path = "/content/v4_stkfold5_epoch3_transformer_3th_000_loss_0.033.ckpt"
model2 = MyModel()
model2.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
model2.cuda()
model_path = "/content/v4_stkfold5_epoch3_transformer_3th_001_loss_0.033.ckpt"
model3 = MyModel()
model3.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
model3.cuda()from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class TestDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, img_paths, transform):
self.img_paths = img_paths
self.transform = transform
def __getitem__(self, index):
image = Image.open(self.img_paths[index])
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
return image, self.img_paths[index]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_paths)from torchvision import transforms
TEST_DIR = "/content/input/data/eval"
submission = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(TEST_DIR, 'info.csv'))
image_dir = os.path.join(TEST_DIR, 'images')
image_paths = [os.path.join(image_dir, img_id) for img_id in submission.ImageID]
valid_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.CenterCrop((400,200)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.56019358, 0.52410121, 0.501457), (0.23318603, 0.24300033, 0.24567522)),
])
dataset = TestDataset(image_paths, valid_transform)
loader = DataLoader(
dataset,
shuffle=False
)
device = torch.device('cuda')model1.eval()
model2.eval()
model3.eval()
pred_result = []
all_predictions = []
for images, path in tqdm(loader):
temp = []
temp.append(path)
with torch.no_grad():
images = images.type(torch.FloatTensor).to(device)
pred1 = model1(images)
pred2 = model2(images)
pred3 = model3(images)
pred = (pred1 + pred2 + pred3)/3
pred = pred.argmax(dim=-1)
temp.append(pred)
all_predictions.extend(pred.cpu().numpy())
pred_result.append(temp)
submission['ans'] = all_predictions
PRETRAINED_MODEL_NAME = "eff_b4_stkkfold_v4_kfold_arcface"
file_name = f"{PRETRAINED_MODEL_NAME}_submission.csv"
submission.to_csv(os.path.join(TEST_DIR, file_name), index=False)
print('test inference is done!')3. Applying Multihead Modeling
Rather than approaching the question as 18 classes classification problem, note823 suggested to approach it as multi-labeling problem. However that was too costly both computationaly and development-wise, so attaching 3 independent fully connected layers have done its job.
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.model = timm.create_model('tf_efficientnet_b4', pretrained=True)
self.model.classifier = nn.Linear(1792, 1024)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 3)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 2)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(1024, 3)
def forward(self, x):
fc_output = self.model(x)
mask = self.fc1(fc_output)
gender = self.fc2(fc_output)
age = self.fc3(fc_output)
return mask, gender, ageEver since the beginning, note823 has been attaching two fully connected layers to the backbone classifier. I was wondering why, but it was later figured out that having another fully connected layer at the end enabled the model to capture the hidden feature of the image.
Other insights
- Validation Loss the was important KPI compared to validation accuracy or validation f1 score. There were some attempts that fixing individual's id for the train dataset and validation dataset to compare model's performance, but I thought this attempt might degrad the randomization of dataset allocation.
- Spending more time on label correction for the train dataset would have improved the accuracy. It was later found that more or less than 100 labels out of 18900 data was wrong.
- validation dataloader shuffle set to False does affect to the model's performance
- Visualization mattered a lot. It was essential to check the model's performance. Checking labels as such code enabled the model has been evaluated properly or not.
def show_images(pred_result_iter, n=5, rows = 1, cols = 5, title = 'Default'):
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10))
plt.suptitle(title, fontsize = 16)
for k in range(n):
img, label = next(pred_result_iter)
label = label.cpu().numpy()[0]
img = Image.open(img[0])
plt.subplot(rows, cols, k+1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title("label:%s"%(label))
pred_result_iter = iter(pred_result)
show_images(pred_result_iter, n=50, rows=5, cols= 10, title='Test Sample')Should have?
- Checking the original label of the dataset should be prioritized rather than attaching the foreign dataset. Team 8 was impressive in terms of using 5-fold trained BEiT models to predict the out-of-folds, check the conflicting votes which is regarded as wrong label.